Health
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neuro developmental disorder characterized by a persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or development. It is typically identified in childhood and can continue into adulthood. ADHD affects various aspects of life, including academic performance, occupational functioning, social interactions, and overall quality of life.
“Comprehensive Healthcare Tips for Successful Surgery:
“Preparing for surgery involves more than just the procedure itself. This guide offers comprehensive healthcare tips to ensure a successful surgery and smooth recovery, from pre-surgery preparations to post-operative care.”
“Jumpstart Your Weight Loss Journey: 5 Easy Tips to Transform Your Life
In the quest for weight loss, simplicity is key. It’s not about drastic measures or overnight transformations; rather, it’s the culmination of consistent, mindful choices that pave the path to success. Here, we unveil five straightforward yet powerful tips to ignite your journey towards shedding pounds and embracing a transformative lifestyle.
1. **Stay Hydrated**: Water is not just a life force; it’s a weight loss ally. By keeping your body hydrated, you not only support its essential functions but also curb unnecessary cravings. So, sip smartly and watch your progress flow.
2. **Eat Mindfully**: In a world of distractions, reclaim the act of eating. Slow down, savor each bite, and tune into your body’s signals. Mindful eating isn’t just about what’s on your plate; it’s about the experience of nourishing your body and soul.
3. **Incorporate More Whole Foods**: Nature’s bounty is abundant with treasures that fuel our bodies with vitality. Load up on vibrant fruits, crisp vegetables, and hearty grains. These wholesome staples not only fill you up but also provide a wealth of nutrients to fuel your journey.
4. **Move Your Body**: Exercise isn’t punishment; it’s a celebration of what your body can do. Find joy in movement, whether it’s a brisk walk in the morning sun or a dance session in your living room. Embrace the rhythm of life and let your body lead the way.
5. **Get Adequate Sleep**: Amidst the hustle and bustle of life, don’t neglect the importance of rest. Quality sleep is the cornerstone of well-being, influencing everything from cravings to metabolism. So, tuck yourself in, dream sweetly, and awaken refreshed for another day of triumphs.
Embark on this journey with courage, knowing that each step brings you closer to the radiant, vibrant version of yourself that awaits at the finish line. Your transformation begins now.
Uterine Fibroids: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
“Community Health Problems: Comprehensive Insights and Strategies for Improvement”
Community health problems refer to the diverse array of issues that affect the health and well-being of populations within defined geographic areas. These issues can be influenced by factors such as socioeconomic status, environmental conditions, cultural beliefs, healthcare access, and public policy. Addressing community health problems requires a comprehensive approach that considers both individual behaviors and broader systemic factors impacting health outcomes.
“Harmony of Life: Exploring the Tapestry of Reproductive Health”
In the quiet embrace of the clinic’s waiting room, Maria felt a mixture of nerves and determination. Her journey to this moment had been marked by uncertainty and hope, a delicate balance between longing and resilience. As she flipped through a pamphlet on fertility treatments, her mind drifted back to the day she had first learned about her infertility.
“It’s not fair,” she had whispered to herself, tears streaming down her cheeks as the doctor gently explained the test results. In that moment, the future she had imagined, filled with laughter and tiny footsteps, seemed to slip away like sand through her fingers.
But today was different. Today, Maria sat with a renewed sense of purpose, a spark of hope flickering within her. She had done her research, sought support from her partner, and made the decision to explore options beyond what she had initially thought possible.
As her name was called, Maria took a deep breath and stood up, ready to embark on the next chapter of her journey. The nurse greeted her with a warm smile, offering reassurance that she was in good hands. Together, they walked down the hallway lined with framed photographs of smiling families—a poignant reminder of the dreams that had been realized within these walls.
In the consultation room, Maria found herself face-to-face with Dr. Nguyen, whose compassionate demeanor instantly put her at ease. They discussed treatment options, from medications to assisted reproductive technologies, each offering a glimmer of hope in the face of adversity.
“It’s not an easy road,” Dr. Nguyen said gently, “but you’re not alone in this journey.”
Maria nodded, her heart filled with gratitude for the supportive team assembled around her. She knew that the path ahead would be filled with challenges and uncertainties, but she also knew that she was taking the first step towards reclaiming her dream of motherhood.
As she left the clinic that day, Maria felt a renewed sense of strength. She glanced up at the sky, where the sun was beginning to set, casting a golden glow over the world. In that moment, she realized that her story was just beginning—a story of resilience, courage, and the unwavering belief in the possibility of new beginnings.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects millions of people worldwide, posing significant challenges to both patients and healthcare systems. This comprehensive description will delve into various aspects of CKD, including its epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic approaches, treatment modalities, and impact on patients’ quality of life.
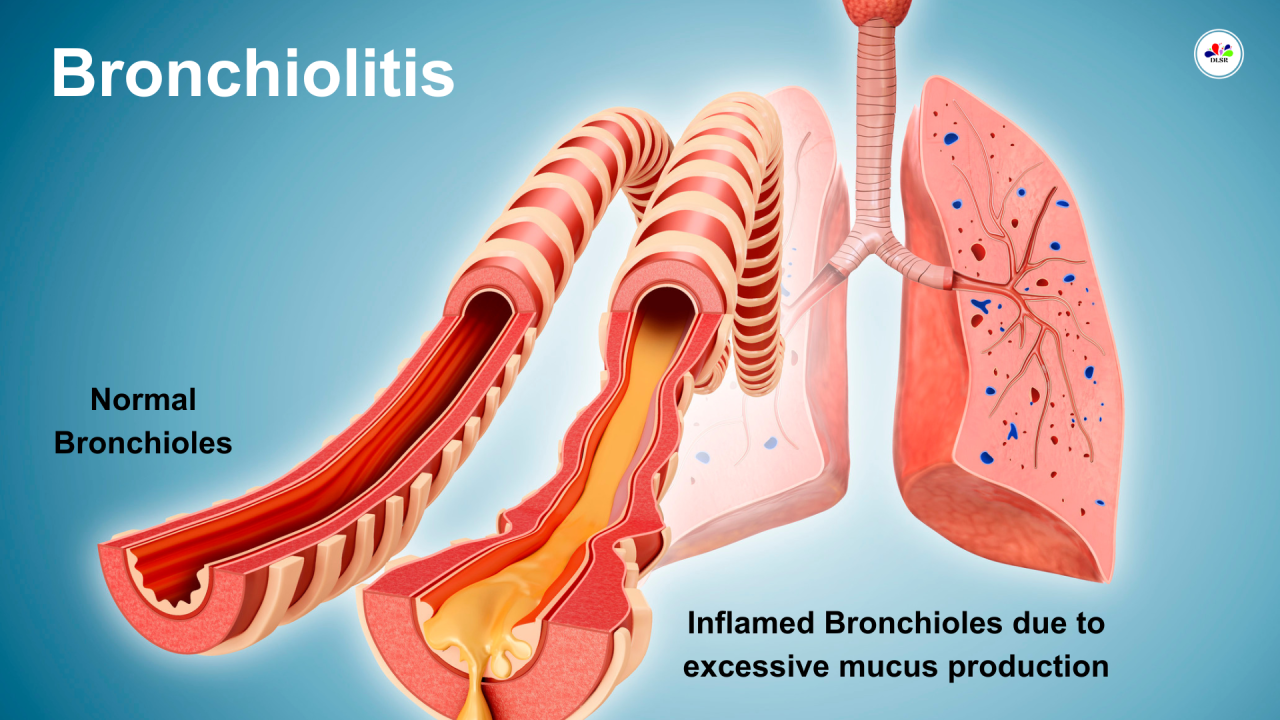
“Bronchiolitis: Comprehensive Overview of Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention”
Bronchiolitis is a common respiratory infection that primarily affects infants and young children, causing inflammation in the smallest air passages of the lungs, called bronchioles. Typically caused by viral infections, especially respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), bronchiolitis presents with symptoms ranging from mild congestion to severe respiratory distress. Treatment often involves supportive care, such as hydration and monitoring oxygen levels, as well as in severe cases, hospitalization. Prevention strategies include good hand hygiene and, where appropriate, the administration of prophylactic medications during peak RSV seasons.
Streptococcal Pharyngitis: A Comprehensive Overview
Streptococcal pharyngitis typically presents with acute onset of symptoms, characterized by a severe sore throat, fever, and painful swallowing. Clinical examination often reveals erythema and swelling of the tonsils, sometimes accompanied by purulent exudate. Tender cervical lymphadenopathy may also be present. These clinical findings, although suggestive, are not specific to streptococcal pharyngitis alone and may overlap with viral causes of pharyngitis.
Diagnosis is crucial to differentiate between bacterial and viral etiologies, as treatment strategies vary significantly. Rapid Antigen Detection Tests (RADTs) are commonly used for quick detection of Group A Streptococcus antigens directly from throat swabs, providing results within minutes. Despite their high specificity, negative RADT results may necessitate confirmatory throat cultures, particularly in cases with high clinical suspicion or in individuals at risk for complications.
Early and accurate diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis is essential to initiate appropriate antibiotic therapy promptly, alleviate symptoms, prevent complications such as rheumatic fever, and reduce transmission within communities.
“Dissociative Disorders Explained: Types, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments”
Understanding Dissociative Disorders: An In-Depth Exploration
Dissociative disorders are a group of mental health conditions that cause significant disruptions in memory, identity, consciousness, and perception. Often linked to severe trauma, particularly in early childhood, these disorders can profoundly affect an individual’s ability to function in daily life. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of dissociative disorders, offering valuable insights into their types, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment.
We explore Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID), characterized by the presence of two or more distinct personality states, as well as Dissociative Amnesia, where individuals experience memory loss for personal information and significant events. The guide also covers Depersonalization/Derealization Disorder, marked by feelings of detachment from oneself and the surroundings, and Dissociative Fugue, involving sudden travel and amnesia.
Through detailed descriptions, practical coping strategies, and the latest research findings, this guide aims to educate health professionals, support individuals living with dissociative disorders, and foster a better understanding of these complex conditions. Join us on this journey to uncover the hidden depths of the human mind and the pathways to healing and recovery.
“Understanding Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & More”
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) presents a complex landscape of emotional instability, impacting how individuals perceive themselves and interact with others. Characterized by intense mood swings, fears of abandonment, and impulsive behaviors, BPD can profoundly affect daily life and relationships. Understanding the underlying causes, such as genetic predisposition, early-life trauma, and neurobiological factors, is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment planning. This comprehensive guide explores these facets in detail, offering insights into evidence-based therapies like Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), as well as strategies for managing co-occurring conditions. By enhancing awareness and empathy, we aim to empower individuals affected by BPD and promote supportive communities that foster recovery and well-being.